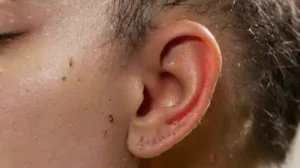
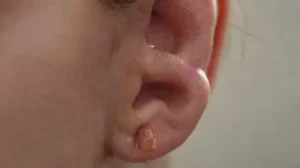
In many professional settings, particularly in healthcare and personal care industries, the sterilization of tools is a critical procedure. Proper sterilization helps prevent the transmission of infections and ensures the safety of both practitioners and clients. When tools are not adequately sterilized, it poses a significant risk of spreading harmful microorganisms that can cause serious health issues.
Despite its importance, sterilization is often overlooked or improperly performed due to time constraints or lack of proper training. This oversight can lead to a cascade of complications, some of which can have long-lasting or severe effects. Therefore, understanding the potential risks associated with poorly sterilized tools is essential for maintaining safety standards.
Risk of bacterial infections
One of the most immediate concerns with inadequately sterilized tools is the risk of bacterial infection. When pathogens survive on contaminated tools, they can invade the body through cuts, abrasions, or mucous membranes. Common bacteria such as Staphylococcus aureus and Streptococcus can cause a range of issues, from minor skin infections to more severe conditions.
Bacterial infections can present with symptoms like redness, swelling, pain, and pus formation. If left untreated, these infections may spread to other parts of the body, leading to more serious complications such as abscesses or systemic infections. Ensuring complete sterilization helps eliminate these microorganisms and reduce infection rates.
Furthermore, resistant strains of bacteria, such as MRSA, are becoming increasingly common and pose additional challenges. These resistant bacteria are harder to treat once an infection occurs. Proper sterilization is a crucial step in preventing the spread of such dangerous microorganisms in clinical or personal settings.
Viral transmission risks
In addition to bacteria, poorly sterilized tools are a significant source of viral transmission. Viruses such as hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and HIV can survive on contaminated surfaces for varying periods, depending on the environment. If tools are not thoroughly sterilized, there’s a danger of inadvertently transmitting these viruses between clients or patients.
The consequences of viral transmission can be severe and long-term. For instance, hepatitis infections can lead to chronic liver disease and increase the risk of liver cancer. HIV transmission, while less common through proper sterilization, remains a critical concern due to the lifelong management required once infected.
Implementing strict sterilization protocols minimizes the risk of viral spread. Regular training and adherence to sterilization standards are essential for professionals working with shared tools, especially in medical or cosmetic industries. Protecting individuals from viral infections depends heavily on these preventative measures.
Skin and soft tissue infections

Contaminated tools can also cause skin and soft tissue infections beyond bacterial and viral concerns. Fungal pathogens, although less common, can lead to conditions such as athlete’s foot or more invasive fungal infections, especially in immunocompromised individuals.
These infections may present with itching, redness, blistering, or ulceration. Sometimes, they may be mistaken for other skin conditions, delaying proper treatment. The risk increases significantly when tools used for skin penetration, such as tattoo needles or piercing equipment, are not fully sterilized.
Preventing skin infections relies on meticulous sterilization processes and hygiene practices. Educating practitioners about proper sterilization techniques can significantly reduce the incidence of these health issues. Clients and patients should also be aware of the importance of certified, sterile tools for their safety.
Cross-contamination concerns
Poor sterilization practices contribute to cross-contamination between clients, practitioners, and surfaces. When tools are reused without adequate sterilization, microorganisms can transfer from one individual to another, creating a cycle of contamination.
Cross-contamination not only spreads infections but also compromises the overall hygiene standards of a facility. It can lead to outbreaks of infectious diseases within clinics, salons, or spas, affecting multiple individuals at once. Maintaining strict sterilization routines is vital to minimize this risk.
Implementing single-use tools where possible and disinfecting reusable instruments thoroughly after each use are effective strategies. Regular monitoring and validation of sterilization process efficacy further safeguard against cross-contamination risks.
Impact on professional reputation
Hospitals, clinics, and personal care businesses rely heavily on their reputation for safety and professionalism. Incidents resulting from the use of improperly sterilized tools can cause damage to their image and erode client trust.
A single outbreak of an infection linked to poor sterilization procedures can lead to legal action, fines, and the loss of clientele. Health authorities may impose sanctions or shut down facilities if standards are consistently not met. Therefore, investing in proper sterilization equipment and training is crucial for long-term success.
Maintaining high sterilization standards demonstrates a commitment to client safety and professionalism. It also aligns with legal and ethical responsibilities, helping organizations avoid costly repercussions associated with preventable health risks.
Legal and ethical implications

Using unsterilized tools can have serious legal consequences. Healthcare providers and personal care practitioners have an obligation to ensure their procedures adhere to established safety protocols. Failure to comply can result in lawsuits, penalties, or licensing issues.
Ethically, practitioners are responsible for protecting the health of their clients. Neglecting proper sterilization protocols compromises this duty and can lead to avoidable harm. Ethical standards in healthcare emphasize the importance of safety, care, and ensuring potential risks are minimized.
Adhering to sterilization guidelines not only safeguards health but also upholds professional integrity. Regular training and audits are essential components in maintaining compliance and demonstrating a commitment to ethical practice.
Cost implications
Inadequate sterilization can lead to significant costs, both immediate and long-term. Treating infections resulting from contaminated tools may require antibiotics, hospitalization, or specialized care, increasing expenses for both clients and providers.
Furthermore, outbreaks of infections due to poor sterilization can result in legal actions, fines, and loss of business. The financial repercussions can outweigh the savings from cutting corners on proper sterilization processes. Investing in quality sterilization equipment and staff training is a cost-effective measure in the long run.
Ultimately, maintaining rigorous sterilization standards protects business operations and supports sustainable growth. It emphasizes that prevention is always more economical than managing preventable health complications.
Conclusion
The proper sterilization of tools is a fundamental practice that ensures safety and hygiene in all industries that involve tool reuse. Neglecting this essential step exposes individuals to unnecessary risks of infections, viral transmissions, and other health complications. Emphasizing consistent and thorough sterilization protocols protects both clients and practitioners, fostering a safer environment.
By understanding the potential consequences of poorly sterilized tools—ranging from health hazards to legal and financial repercussions—professionals can prioritize best practices. Commitment to effective sterilization not only safeguards health but also enhances reputation and trustworthiness in the industry.
In summary, investing in proper sterilization procedures is vital for maintaining high standards of safety and professionalism. It is an ethical obligation that benefits everyone involved and helps prevent avoidable adverse outcomes.