Getting a tattoo is a popular form of expression that has gained widespread acceptance across many cultures. Many individuals are drawn to the vibrant colors and artistic designs that tattoos offer, making it a significant part of personal identity for numerous people. However, as tattoos become more common, concerns about the safety of tattoo inks and potential health implications have also grown.
While most tattoos are considered safe when done in reputable establishments, the long-term effects of certain ink components are not yet fully understood. Researchers and health professionals are increasingly examining how various chemicals in tattoo inks might interact with the body over time, raising questions about possible health risks that could develop years after a tattoo is applied.
Composition of Tattoo Inks
Tattoo inks are complex mixtures primarily consisting of pigments, carrier fluids, and additives. These pigments provide the vibrant colors seen in tattoos and can be made from organic or inorganic materials. While organic pigments are often derived from carbon-based molecules, inorganic pigments might contain metals like iron, titanium, or cadmium.
The carrier fluids, usually water or alcohol-based solutions, help deliver the pigments into the skin. Additives such as preservatives, stabilizers, and antioxidants are also included to improve the stability and longevity of the ink. Despite their importance in maintaining ink quality, some of these substances may pose potential health concerns.
The composition of tattoo inks varies widely among manufacturers, and this variability can impact safety assessments. Regulations differ between countries, which means some inks may contain unknown or untested chemicals. Experts emphasize the importance of choosing certified products to minimize health risks associated with unknown ink components.
Potential Toxicity of Metals and Chemicals
Many tattoo inks contain metals like nickel, chromium, cadmium, and lead to produce certain colors. While these metals are responsible for the vividness and durability of tattoo pigments, they may also have potential toxic effects.
Repeated exposure to these metals through tattoos could lead to allergic reactions, skin irritation, or systemic toxicity. For example, cadmium is a known carcinogen, and lead exposure has been associated with neurological issues. Additionally, some chemical additives used in inks, like preservatives and stabilizers, might induce allergic responses or other adverse health effects.
Research indicates that certain substances in tattoo inks can migrate from the skin into the lymphatic system, potentially resulting in long-term health implications. Although definitive evidence is still lacking, these findings suggest a need for cautious monitoring and regulation of tattoo ink ingredients.
The toxicity of tattoo inks can also depend on individual immune system responses. Some people may experience heightened sensitivity or allergic reactions, making it essential to assess personal risks before getting a tattoo. Continuing research aims to better understand these chemical interactions within the body over time.
Skin Reactions and Allergies

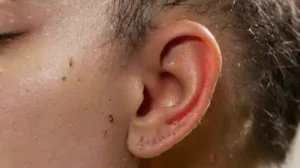
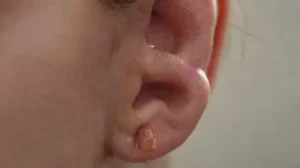
Immediate skin reactions to tattooing are common and usually include redness, swelling, and pain. These symptoms are often a normal part of the healing process, but in some cases, they can be signs of more serious allergic reactions.
Certain pigment ingredients, particularly red and yellow inks, are more likely to cause allergic dermatitis. These reactions might manifest as persistent itching, bumps, or hyperpigmentation at the tattoo site. In severe cases, allergic responses can lead to infection or the need for medical intervention.
Long-term skin reactions include granulomas or the formation of lumps around tattooed areas, which may occur months or even years after the initial tattoo. Ongoing sensitivity to tattoo pigments suggests that some chemicals can trigger immune responses long after the tattoo is done.
Individuals with pre-existing skin conditions or sensitivities are at a higher risk of adverse reactions. It is advisable to consult with a dermatologist or allergy specialist before deciding on a tattoo, especially for people with known sensitivities.
Risk of Infections and Cross-Contamination
Getting a tattoo involves puncturing the skin, which inherently carries a risk of infection if proper hygiene practices are not followed. Unsanitary equipment, contaminated inks, or inadequate sterilization processes can lead to bacterial or viral transmissions.
Serious infections such as hepatitis B and C or even HIV, although rare, have been linked to contaminated tattoo instruments. Ensuring that tattoo artists follow strict hygiene protocols greatly reduces this risk and promotes safer tattooing practices.
In addition to infections, cross-contamination from poorly maintained equipment can introduce pathogens into the skin. Proper sterilization, use of disposable needles, and high-quality inks are essential in minimizing health hazards associated with tattooing.
Vigilance and choosing reputable tattoo studios are crucial steps for individuals concerned about infection risks. Public awareness and regulation play vital roles in maintaining safety standards within the tattoo industry.
Regulatory Standards and Quality Control

Regulatory agencies in many countries have established standards to ensure the safety and quality of tattoo inks. These regulations oversee the composition, labeling, and sale of tattoo products to protect consumers from potentially harmful substances.
Despite these measures, enforcement and compliance vary, leading to continued concerns about adulterated or unregulated inks entering the market. Consumers are encouraged to seek tattoos from licensed and reputable artists who adhere to strict safety guidelines.
Manufacturers are also encouraged to provide transparent ingredient lists and data on chemical safety. Advances in testing methods help identify potentially toxic chemicals in inks before they are widely distributed, improving overall quality control.
Enhanced regulation and increased awareness can significantly reduce health risks associated with tattoo inks. As research progresses, stricter standards may be implemented to further safeguard long-term health.
Long-term Health Monitoring and Research
As the popularity of tattoos continues to grow, so does the need for long-term health monitoring of tattooed individuals. Studies currently underway aim to better understand the potential risks posed by ink components after years or decades.
Medical experts suggest routine check-ups for people with tattoos, especially if experiencing unexplained skin changes or systemic symptoms. Detecting adverse effects early can improve management and treatment outcomes.
The scientific community emphasizes ongoing research to identify safe ink formulations and better understand chemical interactions within the body. Public health agencies support campaigns to raise awareness of potential risks and promote safer tattooing practices.
Investing in long-term studies will help clarify whether certain inks or ingredients should be restricted or reformulated, ultimately improving safety standards for future tattoo recipients.
Conclusion
The safety of tattoo inks and the potential for long-term health effects remain important concerns in the expanding world of body art. While tattoos are generally considered a safe form of expression, the chemicals used in inks can pose health risks that are not fully understood.
It is essential for individuals considering tattoos to research product ingredients, choose reputable tattoo studios, and stay informed about emerging scientific findings. Proper regulation and education are key to ensuring that tattoos remain a safe form of personal expression for everyone.
Ongoing research and stricter standards will hopefully minimize health risks associated with tattoo inks in the future. Increased awareness and precaution can help protect long-term health while allowing people to enjoy the artistic and cultural significance of tattoos.